Foundational OUs - Security #
Accounts, workloads, and data residing in the foundational OUs are typically owned by your centralized Cloud Platform or Cloud Engineering teams made up of cross-functional representatives from your Security, Infrastructure, and Operations teams.
Security OU #
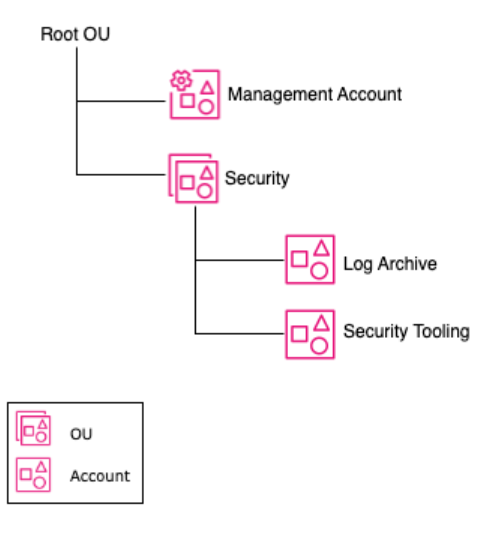
The security OU is used for hosting security-related access and services. The Security OU, its child OUs, and the associated AWS accounts, should be owned and managed by your Security organization.
Recommended accounts #
Log Archive: An AWS account that acts as a consolidation point for security-oriented AWS access and audit logs gathered from all of the AWS accounts in your environment.
Security ReadOnlyAccess (humans): The purpose of this AWS account is to enable your security team members to access other AWS accounts in your AWS environment with read-only permissions in support of auditing, exploratory security testing, and investigations. For example, in the early stages of investigating a suspected security incident, your security team members would first access this AWS account and use a read-only IAM cross-account role, then access other AWS accounts to review and monitor the state of resources.
Security Breakglass (humans): An AWS account that would rarely be used, but available to members of your security team during security incidents. This account would enable extensive write access to your AWS accounts. At the outset of an incident, special authorization would be required for a security team member to gain access. Once an incident has been resolved, the temporary access would be revoked. All access would be logged in detail.
Security Tooling (minimal humans): One or more AWS accounts to host broadly applicable security-oriented workloads and services, tools, and supporting data. Common examples of tools and services configured in this account include an Amazon GuardDuty master account, AWS Security Hub master account, Amazon Detective master account, and third party cloud security monitoring services and tools. Human access to these AWS accounts for administration purposes should be minimized, in favor of using Infrastructure as Code (IaC) and other automated techniques. Where there’s a need for direct human administration, authorized administrators require sufficient write access. Beyond administrative access, additional human access will likely be needed, so that security team members can interact with and potentially configure features of the security services.
Once the central services are in place, we recommend creating OUs that directly relate to building or running your products or services. Many AWS customers build the OUs listed below after establishing the foundation.